k-Nearest Neighbors regression¶
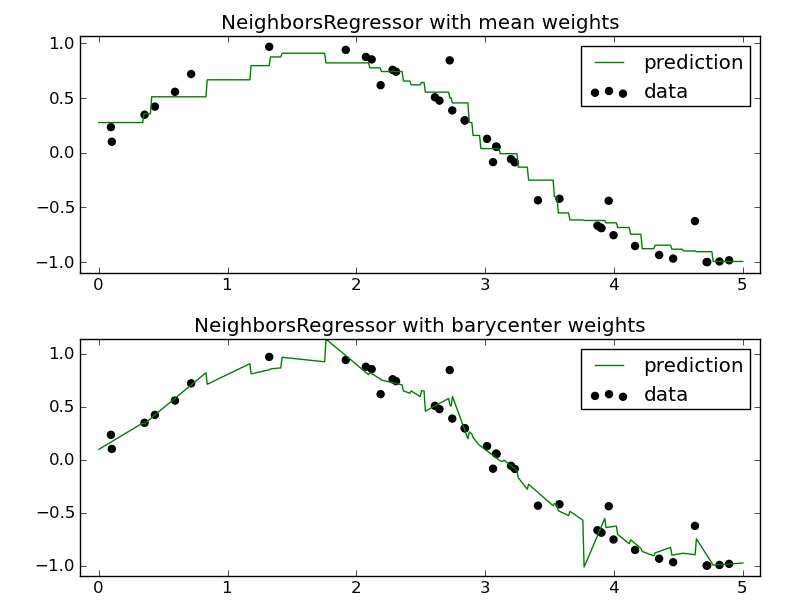
Demonstrate the resolution of a regression problem using a k-Nearest Neighbor and the interpolation of the target using both barycenter and constant weights.
Python source code: plot_neighbors_regression.py
print __doc__
# Author: Alexandre Gramfort <alexandre.gramfort@inria.fr>
# Fabian Pedregosa <fabian.pedregosa@inria.fr>
#
# License: BSD, (C) INRIA
###############################################################################
# Generate sample data
import numpy as np
import pylab as pl
from scikits.learn import neighbors
np.random.seed(0)
X = np.sort(5*np.random.rand(40, 1), axis=0)
T = np.linspace(0, 5, 500)[:, np.newaxis]
y = np.sin(X).ravel()
# Add noise to targets
y[::5] += 1*(0.5 - np.random.rand(8))
###############################################################################
# Fit regression model
for i, mode in enumerate(('mean', 'barycenter')):
knn = neighbors.NeighborsRegressor(n_neighbors=4, mode=mode)
y_ = knn.fit(X, y).predict(T)
pl.subplot(2, 1, 1 + i)
pl.scatter(X, y, c='k', label='data')
pl.plot(T, y_, c='g', label='prediction')
pl.axis('tight')
pl.legend()
pl.title('NeighborsRegressor with %s weights' % mode)
pl.subplots_adjust(0.1, 0.04, 0.95, 0.94, 0.3, 0.28)
pl.show()
