Receiver operating characteristic (ROC)¶
Example of Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) metric to evaluate the quality of the output of a classifier.
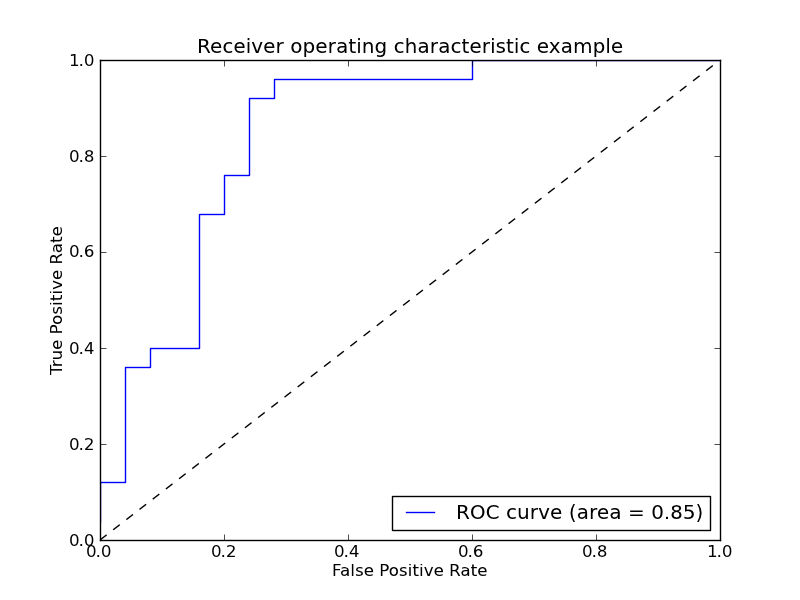
Python source code: plot_roc.py
print __doc__
import random
import numpy as np
import pylab as pl
from scikits.learn import svm, datasets
from scikits.learn.metrics import roc_curve, auc
# import some data to play with
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data
y = iris.target
X, y = X[y!=2], y[y!=2]
n_samples, n_features = X.shape
p = range(n_samples)
random.seed(0)
random.shuffle(p)
X, y = X[p], y[p]
half = int(n_samples/2)
# Add noisy features
X = np.c_[X,np.random.randn(n_samples, 200*n_features)]
# Run classifier
classifier = svm.SVC(kernel='linear', probability=True)
probas_ = classifier.fit(X[:half],y[:half]).predict_proba(X[half:])
# Compute ROC curve and area the curve
fpr, tpr, thresholds = roc_curve(y[half:], probas_[:,1])
roc_auc = auc(fpr, tpr)
print "Area under the ROC curve : %f" % roc_auc
# Plot ROC curve
pl.figure(-1)
pl.clf()
pl.plot(fpr, tpr, label='ROC curve (area = %0.2f)' % roc_auc)
pl.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], 'k--')
pl.xlim([0.0,1.0])
pl.ylim([0.0,1.0])
pl.xlabel('False Positive Rate')
pl.ylabel('True Positive Rate')
pl.title('Receiver operating characteristic example')
pl.legend(loc="lower right")
pl.show()
