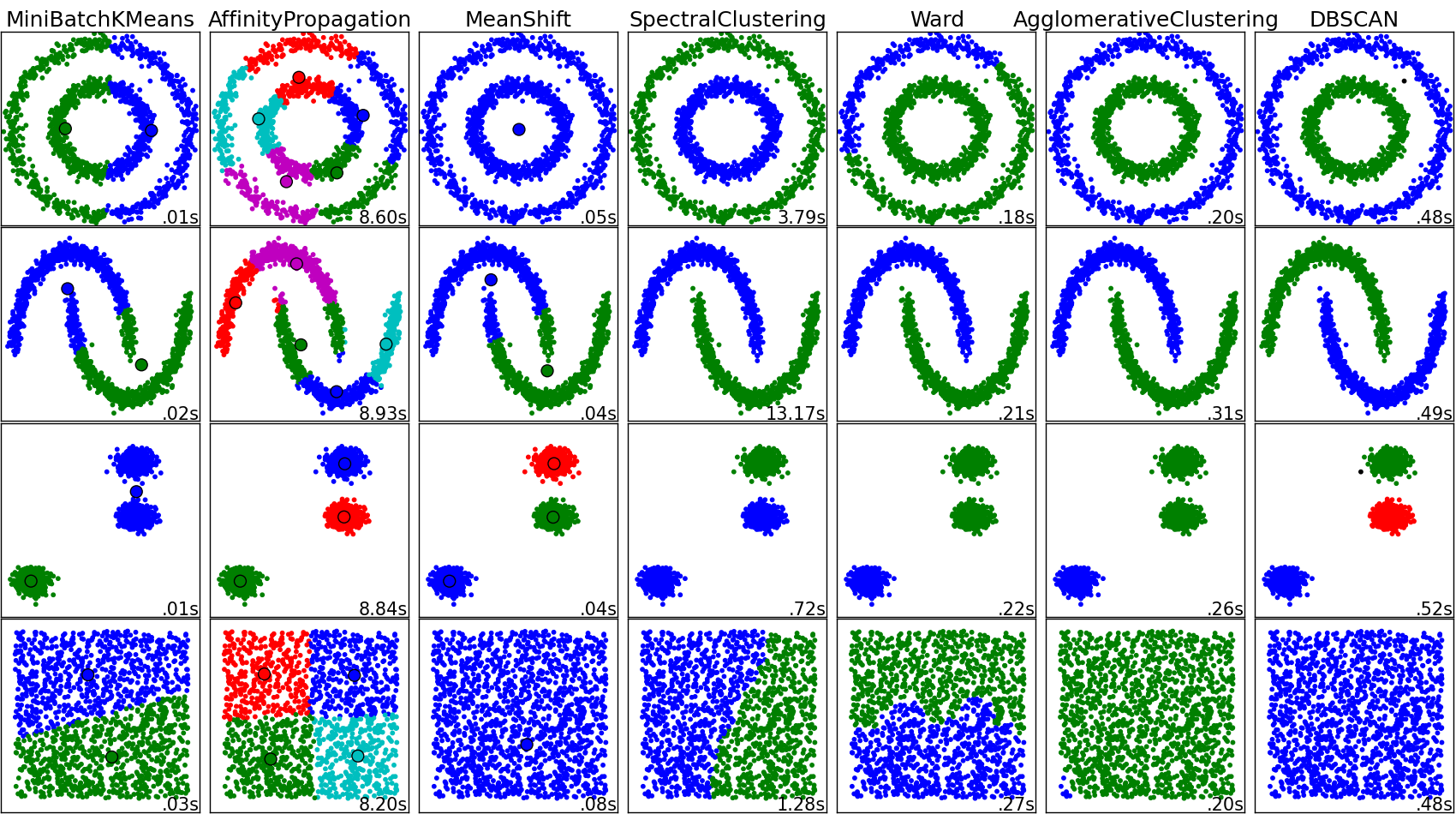
Comparing different clustering algorithms on toy datasets¶
This example aims at showing characteristics of different clustering algorithms on datasets that are “interesting” but still in 2D. The last dataset is an example of a ‘null’ situation for clustering: the data is homogeneous, and there is no good clustering.
While these examples give some intuition about the algorithms, this intuition might not apply to very high dimensional data.
The results could be improved by tweaking the parameters for each clustering strategy, for instance setting the number of clusters for the methods that needs this parameter specified. Note that affinity propagation has a tendency to create many clusters. Thus in this example its two parameters (damping and per-point preference) were set to to mitigate this behavior.
Python source code: plot_cluster_comparison.py
print(__doc__)
import time
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import cluster, datasets
from sklearn.metrics import euclidean_distances
from sklearn.neighbors import kneighbors_graph
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
np.random.seed(0)
# Generate datasets. We choose the size big enough to see the scalability
# of the algorithms, but not too big to avoid too long running times
n_samples = 1500
noisy_circles = datasets.make_circles(n_samples=n_samples, factor=.5,
noise=.05)
noisy_moons = datasets.make_moons(n_samples=n_samples, noise=.05)
blobs = datasets.make_blobs(n_samples=n_samples, random_state=8)
no_structure = np.random.rand(n_samples, 2), None
colors = np.array([x for x in 'bgrcmykbgrcmykbgrcmykbgrcmyk'])
colors = np.hstack([colors] * 20)
plt.figure(figsize=(17, 9.5))
plt.subplots_adjust(left=.001, right=.999, bottom=.001, top=.96, wspace=.05,
hspace=.01)
plot_num = 1
for i_dataset, dataset in enumerate([noisy_circles, noisy_moons, blobs,
no_structure]):
X, y = dataset
# normalize dataset for easier parameter selection
X = StandardScaler().fit_transform(X)
# estimate bandwidth for mean shift
bandwidth = cluster.estimate_bandwidth(X, quantile=0.3)
# connectivity matrix for structured Ward
connectivity = kneighbors_graph(X, n_neighbors=10)
# make connectivity symmetric
connectivity = 0.5 * (connectivity + connectivity.T)
# Compute distances
#distances = np.exp(-euclidean_distances(X))
distances = euclidean_distances(X)
# create clustering estimators
ms = cluster.MeanShift(bandwidth=bandwidth, bin_seeding=True)
two_means = cluster.MiniBatchKMeans(n_clusters=2)
ward = cluster.AgglomerativeClustering(n_clusters=2,
linkage='ward', connectivity=connectivity)
spectral = cluster.SpectralClustering(n_clusters=2,
eigen_solver='arpack',
affinity="nearest_neighbors")
dbscan = cluster.DBSCAN(eps=.2)
affinity_propagation = cluster.AffinityPropagation(damping=.9,
preference=-200)
average_linkage = cluster.AgglomerativeClustering(linkage="average",
affinity="cityblock", n_clusters=2,
connectivity=connectivity)
for name, algorithm in [
('MiniBatchKMeans', two_means),
('AffinityPropagation', affinity_propagation),
('MeanShift', ms),
('SpectralClustering', spectral),
('Ward', ward),
('AgglomerativeClustering', average_linkage),
('DBSCAN', dbscan)
]:
# predict cluster memberships
t0 = time.time()
algorithm.fit(X)
t1 = time.time()
if hasattr(algorithm, 'labels_'):
y_pred = algorithm.labels_.astype(np.int)
else:
y_pred = algorithm.predict(X)
# plot
plt.subplot(4, 7, plot_num)
if i_dataset == 0:
plt.title(name, size=18)
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], color=colors[y_pred].tolist(), s=10)
if hasattr(algorithm, 'cluster_centers_'):
centers = algorithm.cluster_centers_
center_colors = colors[:len(centers)]
plt.scatter(centers[:, 0], centers[:, 1], s=100, c=center_colors)
plt.xlim(-2, 2)
plt.ylim(-2, 2)
plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(())
plt.text(.99, .01, ('%.2fs' % (t1 - t0)).lstrip('0'),
transform=plt.gca().transAxes, size=15,
horizontalalignment='right')
plot_num += 1
plt.show()
Total running time of the example: 61.33 seconds ( 1 minutes 1.33 seconds)

